Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
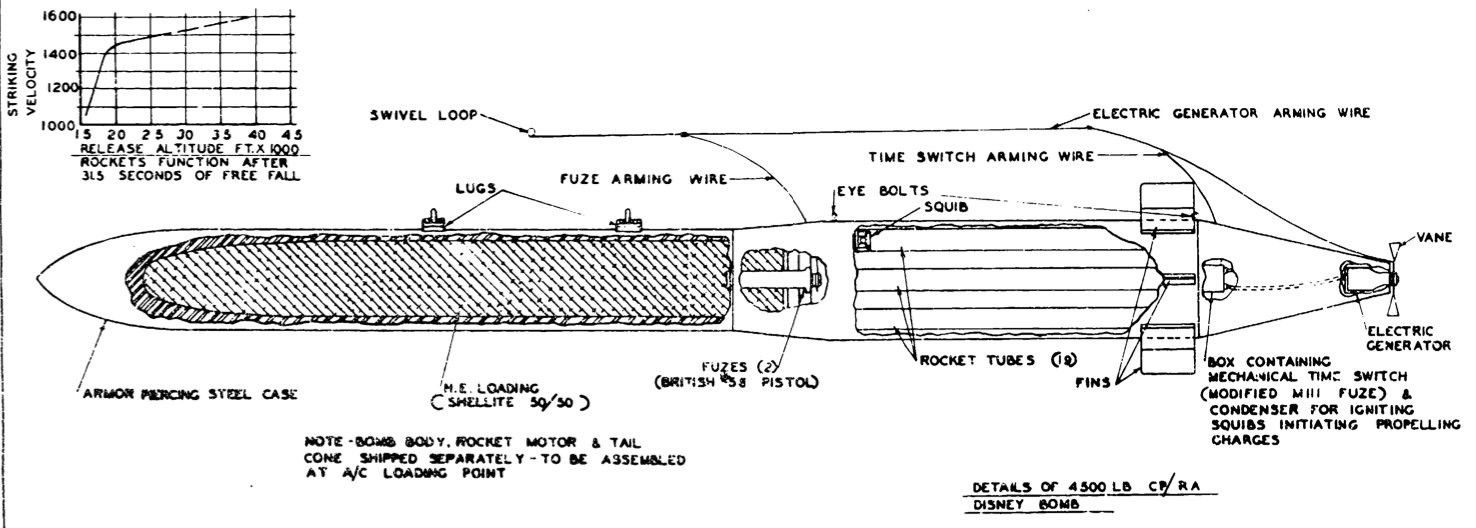
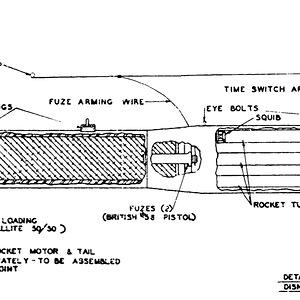
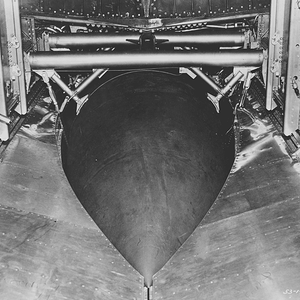
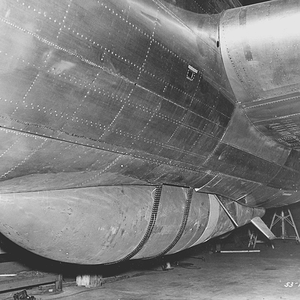
he first Disney attack was against the port of IJmuiden in the Netherlands. This was the site of two separate fortified pens used by the German navy to house their Schnellboote (fast torpedo boats, known to the Allies as "E-boats") and Biber midget submarines. The older structure, codename Schnellbootbunker AY (SBB1), was protected by a 10-foot (3.0 m) thick concrete roof. The newer one, codename Schnellbootbunker BY (SBB2), had 10–12 feet (3.0–3.7 m) of concrete, with a further 2–4-foot (0.61–1.2 m) layer separated by an air–gap.
The E-boats laid up in the shelters during the day, safe from air–attack, and put to sea under cover of night to attack Allied shipping. The pens were priority targets as the torpedo boats they protected were a considerable threat to the supply lines serving Allied forces in western Europe. Since August 1944, the two bunkers had been attacked four times by No. 9 Squadron and No. 617 Squadron of the RAF, with a total of 53 of the five–ton, Tallboy earthquake bombs. There had been numerous other attacks from bombers carrying smaller, conventional bombs.
Nine aircraft of the 92nd Bomb Group, carrying 18 Disneys, attacked Schnellbootbunker BY (SBB2) on 10 February 1945. Royal Navy intelligence learned the concrete had been penetrated, but the pens had been empty at the time of the attack. The 92nd therefore carried out an attack on the SBB1 pen, again with nine aircraft, on 14 March
US Army newsreel, reporting on the first Disney attack on IJmuiden
On 30 March, 36 aircraft from the US Eighth Air Force, including 12 from the 92nd Bomb Group, attacked with Disney bombs the Valentin submarine pens, a massive, bomb–hardened concrete shelter under construction at the small port of Farge, near Bremen in Germany (location: 53°13′00″N 8°30′15″E). The shelter was nearing completion and was to be a factory for the assembly of Type XXI U-boats.[38] Construction had been underway since 1943, using the forced labour of 10,000 concentration–camp prisoners, prisoners–of–war and foreign civilians (Fremdarbeiter) who suffered a high death–rate because of the horrific conditions they worked under.
Valentin's 4.5-metre (15 ft)-thick roof had already been penetrated by two, 10-ton Grand Slam bombs dropped by the RAF three days earlier, on 27 March.] During the Eighth Air Force attack, more than sixty Disneys were launched but only one hit the target with little effect, although installations around the bunker received considerable damage. After the bombing, the Germans made limited attempts to carry out repairs before abandoning the complex; the area was captured by the British Army four weeks later.
On 4 April 1945, 24 B-17s attacked fortified targets in Hamburg. The target was obscured by cloud so radar guidance was used to launch the bombs. A further mission in May 1945 was cancelled. A total of 158 bombs were dropped before the end of the war. No aircraft or aircrew were lost during the four Disney combat missions
The E-boats laid up in the shelters during the day, safe from air–attack, and put to sea under cover of night to attack Allied shipping. The pens were priority targets as the torpedo boats they protected were a considerable threat to the supply lines serving Allied forces in western Europe. Since August 1944, the two bunkers had been attacked four times by No. 9 Squadron and No. 617 Squadron of the RAF, with a total of 53 of the five–ton, Tallboy earthquake bombs. There had been numerous other attacks from bombers carrying smaller, conventional bombs.
Nine aircraft of the 92nd Bomb Group, carrying 18 Disneys, attacked Schnellbootbunker BY (SBB2) on 10 February 1945. Royal Navy intelligence learned the concrete had been penetrated, but the pens had been empty at the time of the attack. The 92nd therefore carried out an attack on the SBB1 pen, again with nine aircraft, on 14 March
US Army newsreel, reporting on the first Disney attack on IJmuiden
On 30 March, 36 aircraft from the US Eighth Air Force, including 12 from the 92nd Bomb Group, attacked with Disney bombs the Valentin submarine pens, a massive, bomb–hardened concrete shelter under construction at the small port of Farge, near Bremen in Germany (location: 53°13′00″N 8°30′15″E). The shelter was nearing completion and was to be a factory for the assembly of Type XXI U-boats.[38] Construction had been underway since 1943, using the forced labour of 10,000 concentration–camp prisoners, prisoners–of–war and foreign civilians (Fremdarbeiter) who suffered a high death–rate because of the horrific conditions they worked under.
Valentin's 4.5-metre (15 ft)-thick roof had already been penetrated by two, 10-ton Grand Slam bombs dropped by the RAF three days earlier, on 27 March.] During the Eighth Air Force attack, more than sixty Disneys were launched but only one hit the target with little effect, although installations around the bunker received considerable damage. After the bombing, the Germans made limited attempts to carry out repairs before abandoning the complex; the area was captured by the British Army four weeks later.
On 4 April 1945, 24 B-17s attacked fortified targets in Hamburg. The target was obscured by cloud so radar guidance was used to launch the bombs. A further mission in May 1945 was cancelled. A total of 158 bombs were dropped before the end of the war. No aircraft or aircrew were lost during the four Disney combat missions