Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
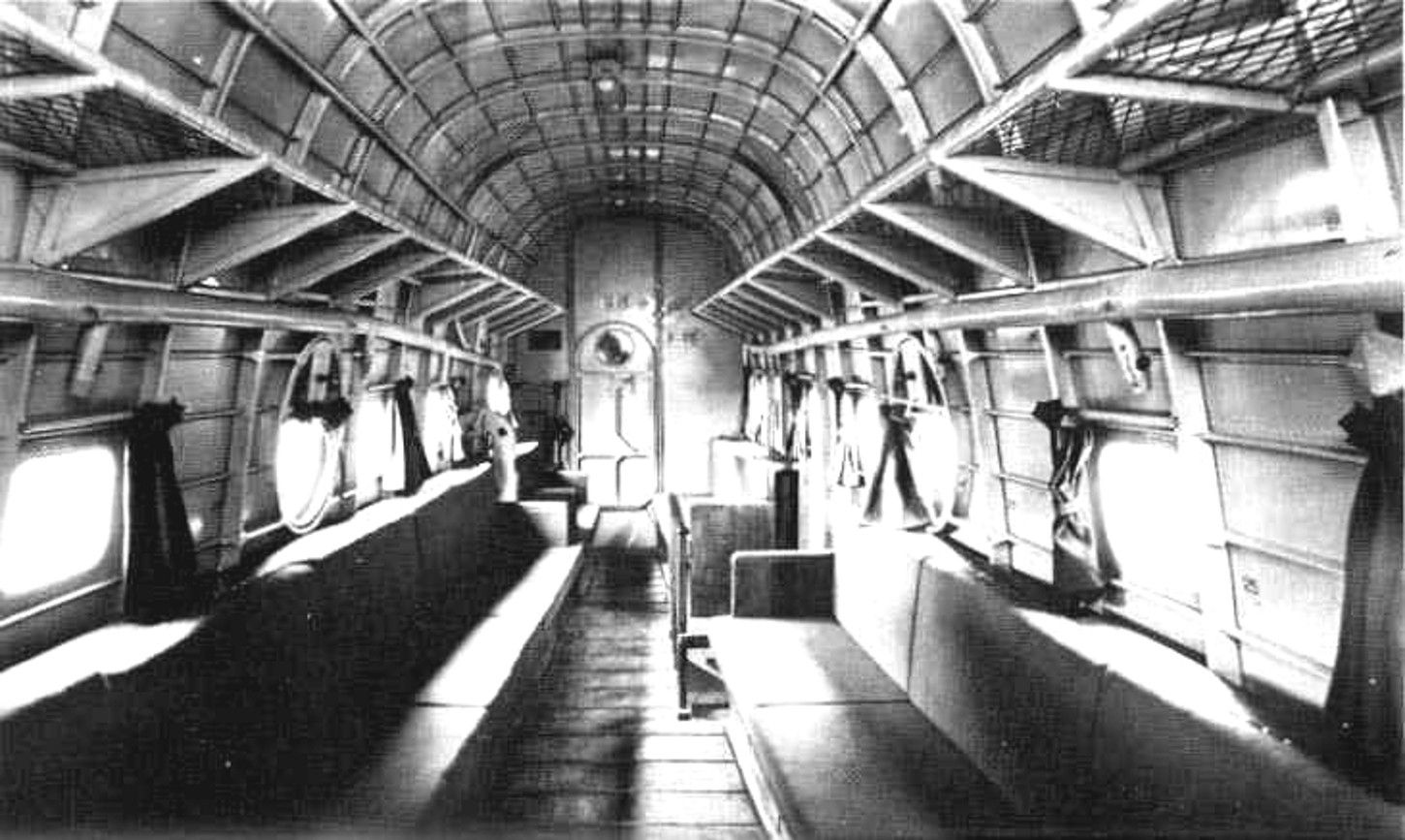
H8K1 Experimental Type 13 Large-sized Flying boat (13試大型飛行艇 13-Shi Ōgata Hikōtei) One prototype and four supplementary prototypes. Prototype was mounted Mitsubishi Mk4A Kasei 11 engines, supplementary prototype was mounted Mitsubishi MK4B Kasei 12 engines. Supplementary prototypes were renamed Type 2 Flying Boat Model 11 on 5 February 1942. Prototype was rebuilt to H8K1-L in November 1943. H8K1 Type 2 Flying boat, Model 11 (二式飛行艇11型 Nishiki Hikōtei 11-gata) Developed on 5 February 1942. First operative model of series, 12 produced. Mounted Mitsubishi MK4B Kasei 12 engines. H8K1-L Type 2 Transport Flying Boat (二式輸送艇 Nishiki Yusōtei) Rebuilt from H8K1 prototype. Fitted augment exhausts. Up to 41 passengers. H8K2 Type 2 Flying boat, Model 12 (二式飛行艇12型 Nishiki Hikōtei 12-gata) Developed on 26 June 1943. Mounted Mitsubishi MK4Q Kasei 22 engines and improved tail gun turret. Latter batch was equipped with Air-to-Surface-Vessel search radar, and removed side gun blisters. 112 produced.[13] H8K2-L Seikū ("Clear Sky"), Model 32 (晴空32型 Seikū 32-gata) Transport version of H8K2. Initial named Type 2 Transport Flying Boat, Model 32. Armaments were 1 × forward-firing 20 mm cannon and 1 × rearward-firing 13 mm machine gun. Up to 64 passengers. H8K3 Provisional name Type 2 Flying Boat, Model 22 (仮称二式飛行艇22型 Kashō Nishiki Hikōtei 22-gata) Experimental version, H8K2 modified. Equipped with retractable floats in wingtips, fowler flaps, sliding hatch side gun locations in place of the blisters and a retractable dorsal turret, all in an effort to increase speed, two prototypes only (work number 596 and 597). H8K4 Provisional name Type 2 Flying Boat, Model 23 (仮称二式飛行艇23型 Kashō Nishiki Hikōtei 23-gata) H8K3 re-engined with 1,825 hp MK4T Mitsubishi Kasei 25b engines, two converted from H8K3. H8K4-L Provisional name Seikū, Model 33 (仮称晴空33型 Kashō Seikū 33-gata) Transport version of H8K4. Only a project, because all H8K4s were lost in March 1945. G9K Proposed land-based attack bomber variant, only a project.