Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
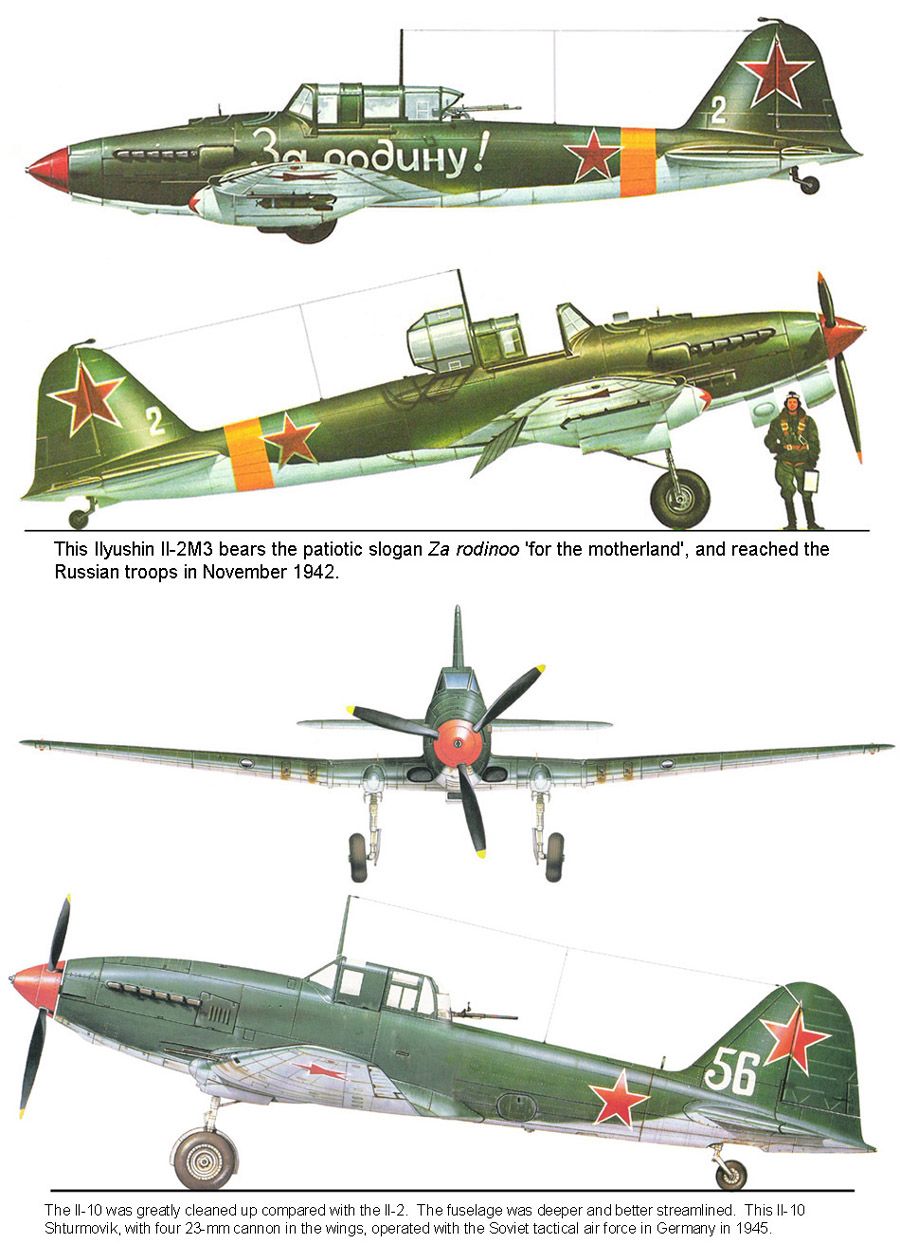
The Ilyushin Il-2 was a ground-attack aircraft (Shturmovik) in the Second World War, produced by the Soviet Union in very large numbers. In combination with its successor, the Ilyushin Il-10, a total of 42,330 were built, making it the single most produced military aircraft design in all of aviation history, as well as one of the most produced piloted aircraft in history along with the Cessna 172 and the Polikarpov Po-2. It is regarded as the best ground attack aircraft of World War II. It was a prominent aircraft for tank killing with its accuracy in dive bombing and its 37mm guns being able to penetrate tanks' thin back armour.
October 1944, the Il-10 first entered service with training units in the Soviet Air Force. In January 1945, the first Il-10 combat unit entered service with the 78th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment, but it did not enter action due to unfinished training. However, three other Il-10 units managed to take part in the final combat actions of World War II in Europe. They were the 571st Assault Aviation Regiment (from 15 April 1945), the 108th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (from 16 April 1945), and the 118th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (on 8 May 1945). About a dozen aircraft were destroyed by flak or engine breakdowns, but the Il-10 appeared to be a successful design. One was shot down by an Fw 190 fighter, but a crew of the 118th Regiment shot down another Fw 190 and probably damaged another. On 10 May 1945, the day after the official Soviet end of the war, (Victory Day), there were 120 serviceable Il-10s in Soviet Air Force combat units, and 26 disabled ones.
After the USSR reentered the war against the Empire of Japan, with the invasion of Manchuria, from 9 August 1945, one Il-10 unit, the 26th Assault Aviation Regiment of the Pacific Navy Aviation, was used in combat in the Korean Peninsula, attacking Japanese ships in Rasin and rail transports.
Info: Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ilyushin_Il-2
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ilyushin_Il-10
Profiles:
Aircraft Of World War 2
Published by Octopus Books Ltd.
Great Aircraft of the World
Published by Colour Library Books Ltd.
October 1944, the Il-10 first entered service with training units in the Soviet Air Force. In January 1945, the first Il-10 combat unit entered service with the 78th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment, but it did not enter action due to unfinished training. However, three other Il-10 units managed to take part in the final combat actions of World War II in Europe. They were the 571st Assault Aviation Regiment (from 15 April 1945), the 108th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (from 16 April 1945), and the 118th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (on 8 May 1945). About a dozen aircraft were destroyed by flak or engine breakdowns, but the Il-10 appeared to be a successful design. One was shot down by an Fw 190 fighter, but a crew of the 118th Regiment shot down another Fw 190 and probably damaged another. On 10 May 1945, the day after the official Soviet end of the war, (Victory Day), there were 120 serviceable Il-10s in Soviet Air Force combat units, and 26 disabled ones.
After the USSR reentered the war against the Empire of Japan, with the invasion of Manchuria, from 9 August 1945, one Il-10 unit, the 26th Assault Aviation Regiment of the Pacific Navy Aviation, was used in combat in the Korean Peninsula, attacking Japanese ships in Rasin and rail transports.
Info: Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ilyushin_Il-2
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ilyushin_Il-10
Profiles:
Aircraft Of World War 2
Published by Octopus Books Ltd.
Great Aircraft of the World
Published by Colour Library Books Ltd.