Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
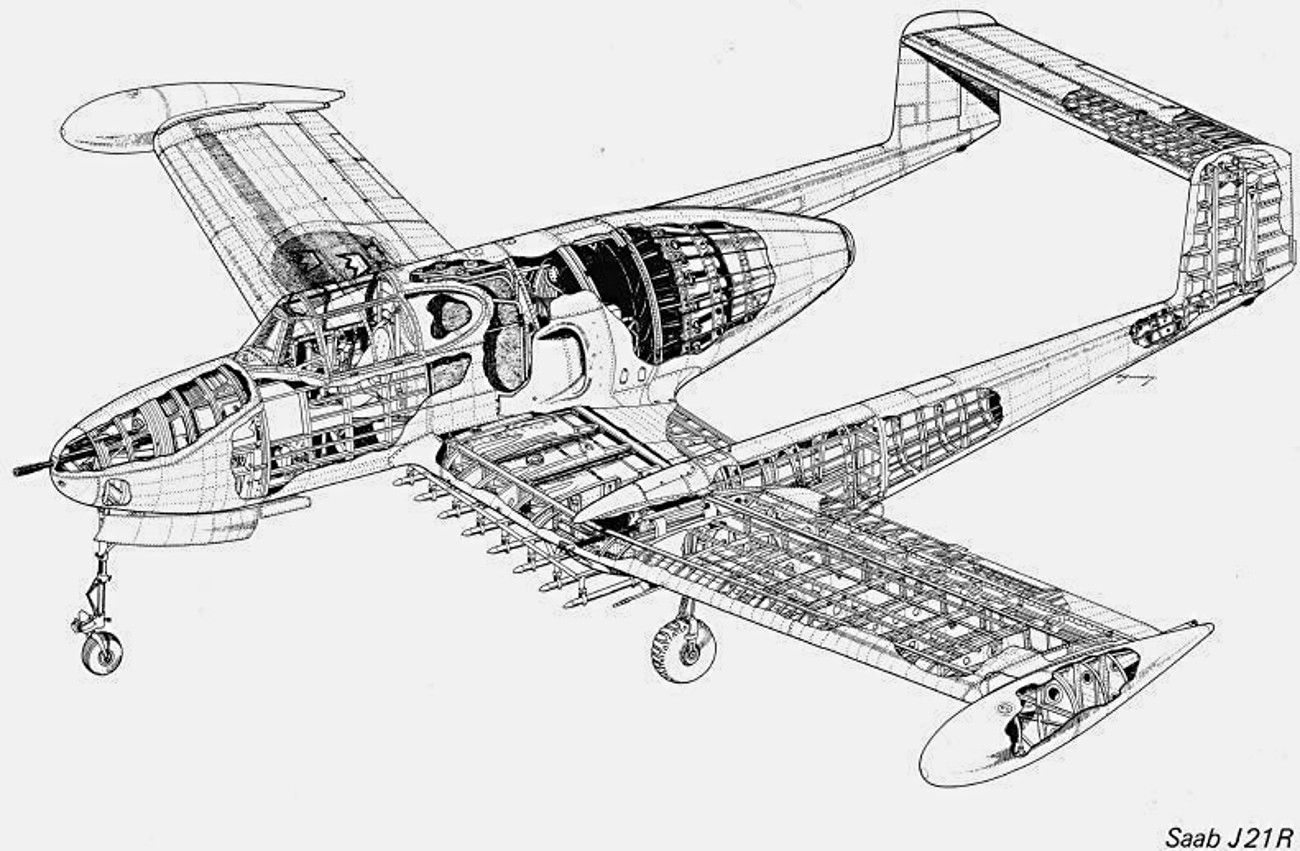
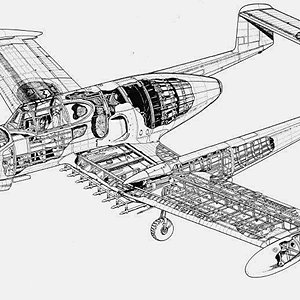
Design and developmentThe 21R was powered by a de Havilland Goblin 3 turbojet (RM 1) and was Sweden's first jet-powered aircraft to be developed and built domestically.
There were quite a few differences between the 21A and the 21R, aside from the method of propulsion. The most notable difference was that the tailplane was raised to the top of the fins, moving it out of the way of the jet blast.
[edit] Operational historyThe first prototype Saab 21R first flew on 10 March 1947,[1] just after the Second World War. The aircraft first entered into service with F 10 in August 1950. Although the type was originally intended as a fighter aircraft, a newly developed fighter, the Saab J 29 first flew in October 1948, the number to be produced was halved from 120 to 60, and eventually all 21Rs were converted to attack aircraft as A 21RA or the A 21RB depending on the engine type.
[edit] VariantsJ 21RA / A 21RA
First production series, powered by British-built engines, 34 built in 1950 (including four prototypes), retired in 1953.[2]
J 21RB / A 21RB
Second production series, powered by Swedish-built engines, 30 built between 1950 and 1952, retired in 1956.
[edit] Operators Sweden
Swedish Air Force
[edit] Specifications (Saab 21RA)Data from Attack and Interceptor Jets[3]
General characteristics
Crew: One
Length: 10.45 m (34 ft 3 in)
Wingspan: 11.37 m (37 ft 4 in)
Height: 2.90 m (9 ft 8 in)
Empty weight: 3,200 kg (7,055 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 5,000 kg (11,023 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × de Havilland Goblin 2 turbojet, 13.8 kN (3,100 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: 800 km/h (497 mph)
Range: 720 km (450 mi)
Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,400 ft)
Takeoff roll: 650 m (2,133 ft)
Armament
1x 20 mm Bofors Cannon
4x 13.2 mm M/39A Heavy machine guns
Centerline pod for an additional 8x 13.2 mm M/39A Heavy machine guns
Wing racks for either: 10x 100 mm or 5x 180 mm Bofors rockets, or 10x 80 mm anti-tank rockets.
There were quite a few differences between the 21A and the 21R, aside from the method of propulsion. The most notable difference was that the tailplane was raised to the top of the fins, moving it out of the way of the jet blast.
[edit] Operational historyThe first prototype Saab 21R first flew on 10 March 1947,[1] just after the Second World War. The aircraft first entered into service with F 10 in August 1950. Although the type was originally intended as a fighter aircraft, a newly developed fighter, the Saab J 29 first flew in October 1948, the number to be produced was halved from 120 to 60, and eventually all 21Rs were converted to attack aircraft as A 21RA or the A 21RB depending on the engine type.
[edit] VariantsJ 21RA / A 21RA
First production series, powered by British-built engines, 34 built in 1950 (including four prototypes), retired in 1953.[2]
J 21RB / A 21RB
Second production series, powered by Swedish-built engines, 30 built between 1950 and 1952, retired in 1956.
[edit] Operators Sweden
Swedish Air Force
[edit] Specifications (Saab 21RA)Data from Attack and Interceptor Jets[3]
General characteristics
Crew: One
Length: 10.45 m (34 ft 3 in)
Wingspan: 11.37 m (37 ft 4 in)
Height: 2.90 m (9 ft 8 in)
Empty weight: 3,200 kg (7,055 lb)
Max takeoff weight: 5,000 kg (11,023 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × de Havilland Goblin 2 turbojet, 13.8 kN (3,100 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: 800 km/h (497 mph)
Range: 720 km (450 mi)
Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,400 ft)
Takeoff roll: 650 m (2,133 ft)
Armament
1x 20 mm Bofors Cannon
4x 13.2 mm M/39A Heavy machine guns
Centerline pod for an additional 8x 13.2 mm M/39A Heavy machine guns
Wing racks for either: 10x 100 mm or 5x 180 mm Bofors rockets, or 10x 80 mm anti-tank rockets.