Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Design and development
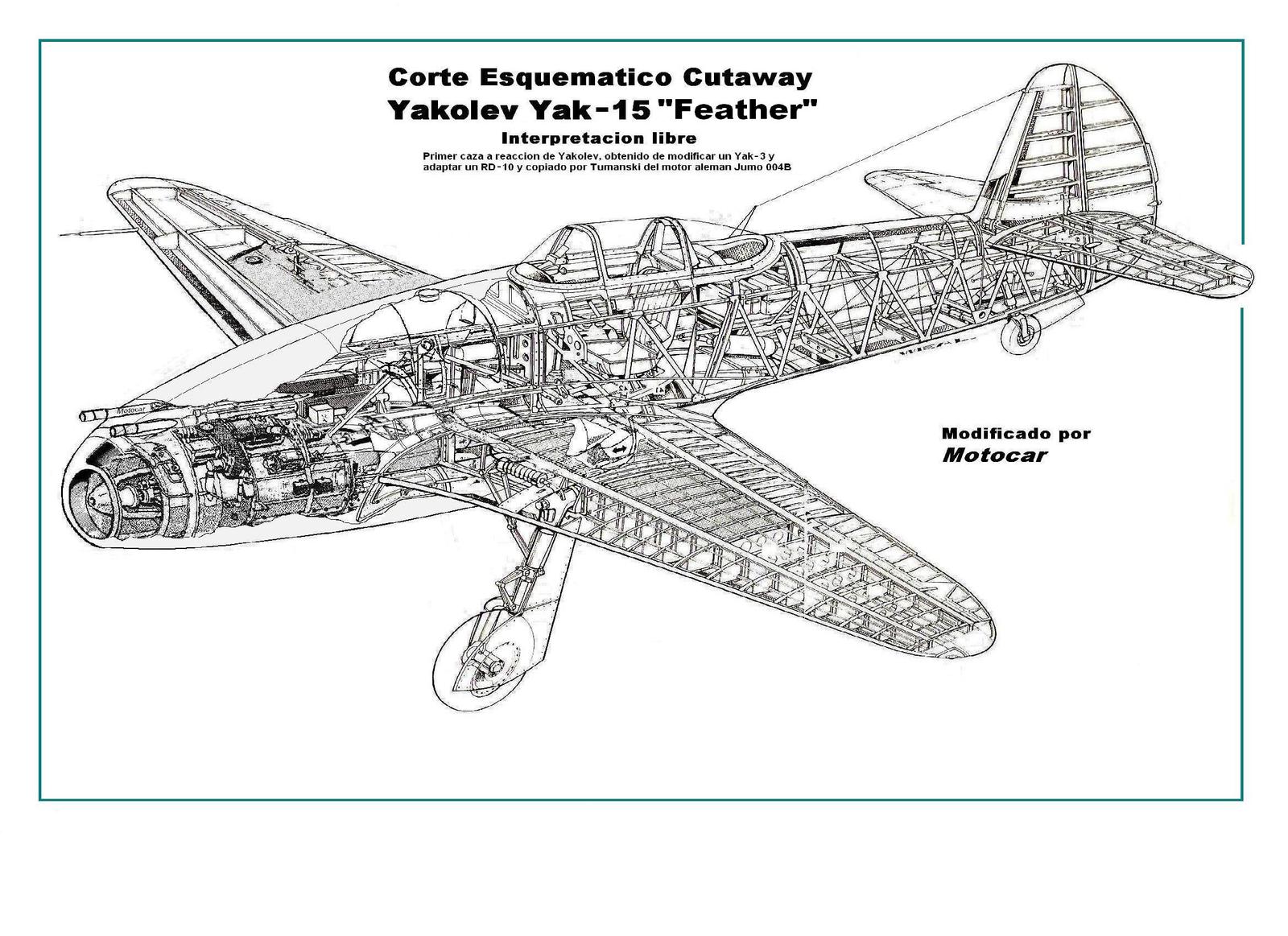
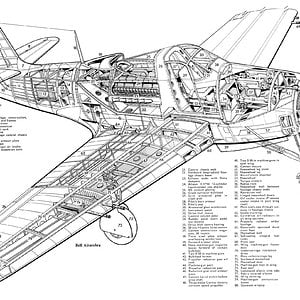
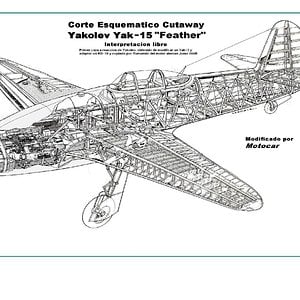
In addition, the main gear had to be redesigned to place the wheels behind the aircraft's center of gravity. The main gear were moved behind the front spar, and when retracted they filled most of the space between the spars. This caused a major redesign of the fuel tanks and reduced their capacity to just 680 liters (150 gallons). This necessitated the addition of two 200 liter (44 gallon) jettisonable tanks, which hung under the tip of each wing. The addition of the tip tanks required a redesign of the structure of the wing so that the aircraft could still maintain a load bearing of 12g. The vertical stabilizer was enlarged and a periscope was also added above the windscreen on most series aircraft. Armament, systems, and equipment were virtually unchanged.[2]
[edit] Operational history
Yak-17 was first publicly displayed at the Soviet Aviation Day of 1949, at Tushino.
In operation the Yak-17 had most of the same faults as its predecessor, including relatively low speed and range, and an unreliable engine (still based upon the German Junkers Jumo 004) with a complicated starting procedure. On the other hand, its handling was very simple, and similar to popular propeller fighters such as the Yak-3 and Yak-9. This made it an excellent transitional machine to jet fighters. As a result, the trainer version Yak-17UTI accounted for the majority of production, and almost all series-built Yak-17s were of this tandem, dual-control trainer version, which filled an important need in all Soviet air arms.[2]
Surviving Yak-17 can be viewed at the Central Air Force Museum at Monino. outside of Moscow and the Prague Aviation Museum at Kbely Airport, near Prague, Czech Republic. Surviving Yak-17UTI include one example at the Polish Aviation Museum near Krakow and the Chinese Aviation Museum, near Beijing.
Specifications (Yak-17)
General characteristics
Crew: one, pilot
Length: 8.70 m (28 ft 6 in)
Wingspan: 9.20 m (30 ft 2 in)
Height: 2.30 m (7 ft 7 in)
Wing area: 14.9 m² (160 ft²)
Empty weight: 2,081 kg (4,578 lb)
Loaded weight: 2,890 kg (6,358 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 3,240 kg (7,128 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × Klimov RD-10A turbojet, 8.9 kN (2,000 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: 748 km/h (468 mph)
Range: 395 km (247 miles)
Service ceiling: 12,750 m (41,820 ft)
Rate of climb: 12 m/s (2362 ft/min)
Wing loading: 194 kg/m² (40 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.31
Armament
2x 23 mm Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 machine guns with 60 rounds each
In addition, the main gear had to be redesigned to place the wheels behind the aircraft's center of gravity. The main gear were moved behind the front spar, and when retracted they filled most of the space between the spars. This caused a major redesign of the fuel tanks and reduced their capacity to just 680 liters (150 gallons). This necessitated the addition of two 200 liter (44 gallon) jettisonable tanks, which hung under the tip of each wing. The addition of the tip tanks required a redesign of the structure of the wing so that the aircraft could still maintain a load bearing of 12g. The vertical stabilizer was enlarged and a periscope was also added above the windscreen on most series aircraft. Armament, systems, and equipment were virtually unchanged.[2]
[edit] Operational history
Yak-17 was first publicly displayed at the Soviet Aviation Day of 1949, at Tushino.
In operation the Yak-17 had most of the same faults as its predecessor, including relatively low speed and range, and an unreliable engine (still based upon the German Junkers Jumo 004) with a complicated starting procedure. On the other hand, its handling was very simple, and similar to popular propeller fighters such as the Yak-3 and Yak-9. This made it an excellent transitional machine to jet fighters. As a result, the trainer version Yak-17UTI accounted for the majority of production, and almost all series-built Yak-17s were of this tandem, dual-control trainer version, which filled an important need in all Soviet air arms.[2]
Surviving Yak-17 can be viewed at the Central Air Force Museum at Monino. outside of Moscow and the Prague Aviation Museum at Kbely Airport, near Prague, Czech Republic. Surviving Yak-17UTI include one example at the Polish Aviation Museum near Krakow and the Chinese Aviation Museum, near Beijing.
Specifications (Yak-17)
General characteristics
Crew: one, pilot
Length: 8.70 m (28 ft 6 in)
Wingspan: 9.20 m (30 ft 2 in)
Height: 2.30 m (7 ft 7 in)
Wing area: 14.9 m² (160 ft²)
Empty weight: 2,081 kg (4,578 lb)
Loaded weight: 2,890 kg (6,358 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 3,240 kg (7,128 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × Klimov RD-10A turbojet, 8.9 kN (2,000 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed: 748 km/h (468 mph)
Range: 395 km (247 miles)
Service ceiling: 12,750 m (41,820 ft)
Rate of climb: 12 m/s (2362 ft/min)
Wing loading: 194 kg/m² (40 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.31
Armament
2x 23 mm Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 machine guns with 60 rounds each