Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Name: Graf Zeppelin
Namesake: Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin
Ordered: 16 November 1935
Laid down: 28 December 1936
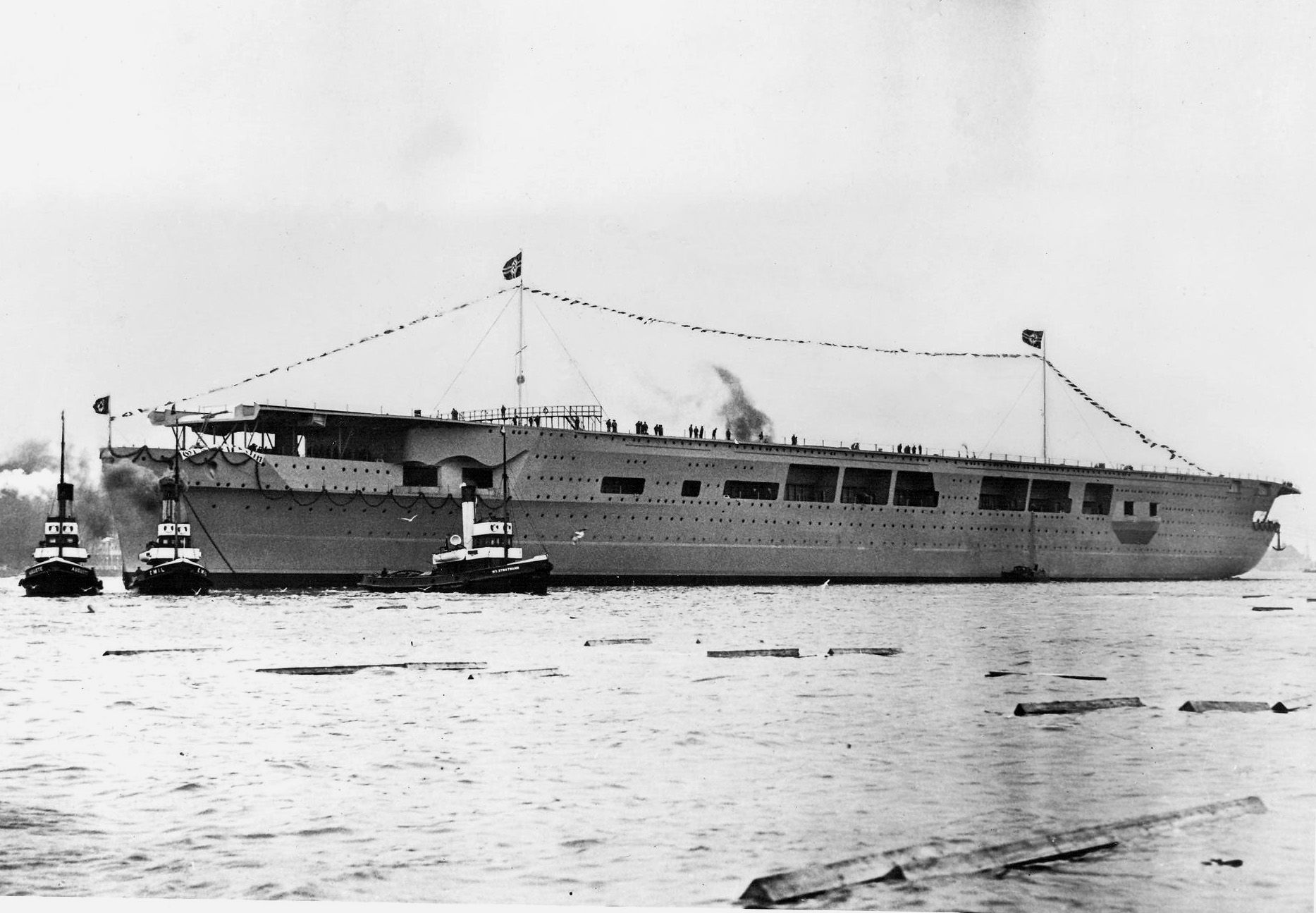
Launched: 8 December 1938
Fate: Sunk as a target ship on 16 August 1947
General characteristics
Displacement: 33,550 tonnes
Length: 262.5 m (861 ft 3 in)
Beam: 31.5 m (103 ft 4 in)
Draft: 7.6 m (24 ft 11 in)
Propulsion: Geared turbines, 200,000 WPS (147,000 kW), four screws
Speed: 35 kn (65 km/h)
Range: 14,816 km (8,000 nmi) at 19 kn (35 km/h)
Complement: 1,720 crew
306 flight personnel
Armament: 16 × 15 cm SK C/28 guns
12 × Flak (10.5 cm)
22 × 3.7 cm SK C/30 (AA)
28 × Flak (2.0 cm)
Aircraft carried: Proposed complement of 42[1]
1930 proposal:
30 fighters & 12 dive bombers
1939 proposal:
12 fighters & 30 dive bombers[1]
See main article for details of proposed aircraft types.
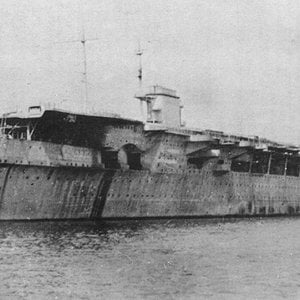
German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin was the lead ship in a class of two carriers ordered by the Kriegsmarine. She was the only aircraft carrier launched by Germany during World War II and represented part of the Kriegsmarine's attempt to create a well-balanced oceangoing fleet, capable of projecting German naval power far beyond the narrow confines of the Baltic and North Seas. Construction was ordered on 16 November 1935 and her keel was laid down on 28 December 1936 by Deutsche Werke at Kiel. Named in honor of Graf (Count) Ferdinand von Zeppelin, the ship was launched on 8 December 1938 but was not completed and was never operational.
Namesake: Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin
Ordered: 16 November 1935
Laid down: 28 December 1936
Launched: 8 December 1938
Fate: Sunk as a target ship on 16 August 1947
General characteristics
Displacement: 33,550 tonnes
Length: 262.5 m (861 ft 3 in)
Beam: 31.5 m (103 ft 4 in)
Draft: 7.6 m (24 ft 11 in)
Propulsion: Geared turbines, 200,000 WPS (147,000 kW), four screws
Speed: 35 kn (65 km/h)
Range: 14,816 km (8,000 nmi) at 19 kn (35 km/h)
Complement: 1,720 crew
306 flight personnel
Armament: 16 × 15 cm SK C/28 guns
12 × Flak (10.5 cm)
22 × 3.7 cm SK C/30 (AA)
28 × Flak (2.0 cm)
Aircraft carried: Proposed complement of 42[1]
1930 proposal:
30 fighters & 12 dive bombers
1939 proposal:
12 fighters & 30 dive bombers[1]
See main article for details of proposed aircraft types.
German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin was the lead ship in a class of two carriers ordered by the Kriegsmarine. She was the only aircraft carrier launched by Germany during World War II and represented part of the Kriegsmarine's attempt to create a well-balanced oceangoing fleet, capable of projecting German naval power far beyond the narrow confines of the Baltic and North Seas. Construction was ordered on 16 November 1935 and her keel was laid down on 28 December 1936 by Deutsche Werke at Kiel. Named in honor of Graf (Count) Ferdinand von Zeppelin, the ship was launched on 8 December 1938 but was not completed and was never operational.