Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Design and development
In 1942, John K. Northrop conceived the XP-79 as a high-speed rocket-powered flying-wing fighter aircraft.
In January 1943, a contract for three prototypes designation XP-79 was issued by the United States Army Air Forces.
To test the radical design, glider prototypes were built. One designated MX-324 was towed into the air on 5 July 1944 by a P-38 making it the first US-built rocket-powered aircraft to fly.[1]
Originally, it was planned to use a 2,000 lbf (9 kN) thrust XCALR-2000A-1 "rotojet" rocket motor supplied by Aerojet that used monoethyl aniline and red fuming nitric acid; because of the corrosive and toxic nature of the liquids, the XP-79 was built using a welded magnesium alloy monocoque structure (to protect the pilot if the aircraft was damaged in combat) with a ⅛ in (3 mm) skin thickness at the trailing edge and a ¾ in (19 mm) thickness at the leading edge. However, the rocket motor configuration using canted rockets to drive the turbopumps was unsatisfactory and the aircraft was, subsequently fitted with two Westinghouse 19-B (J30) turbojets instead. This led to changing the designation to XP-79B. After the failure of the rocket motor, further development of the first two prototypes, ended.
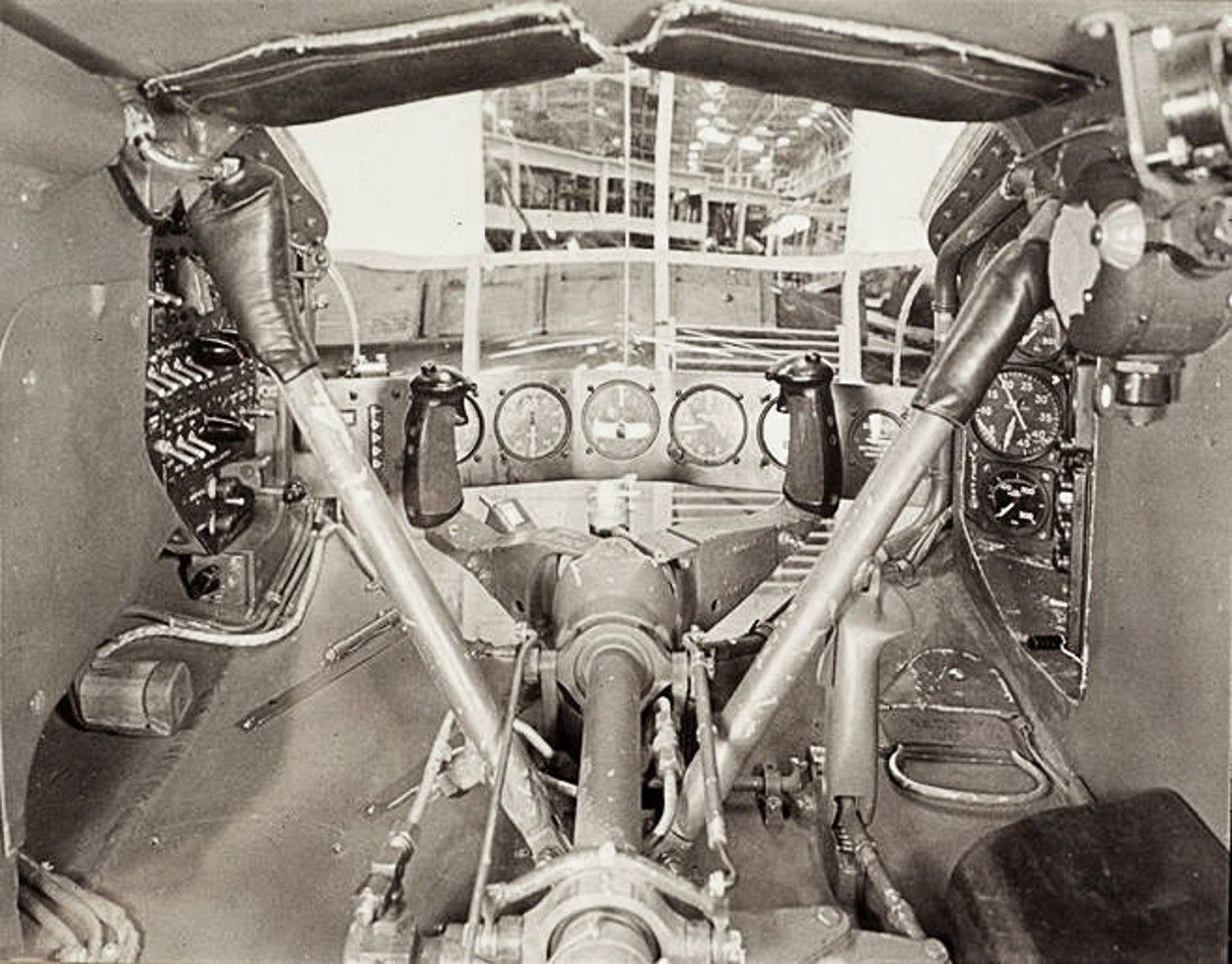
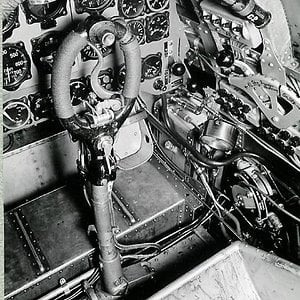
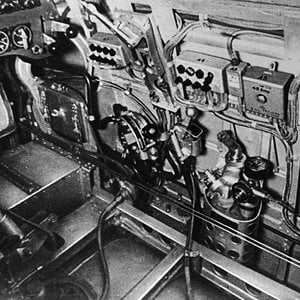
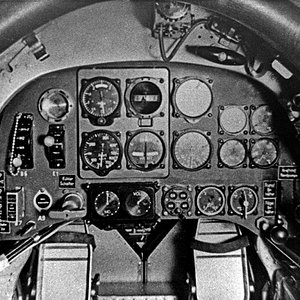
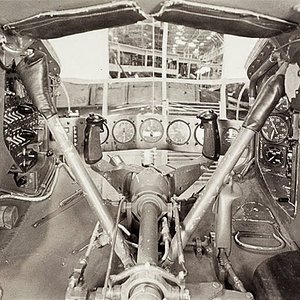
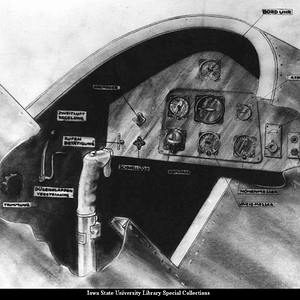
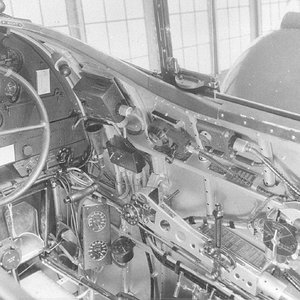
The pilot controlled the XP-79 through a tiller bar and rudders mounted below; intakes mounted at the wingtips supplied air for the unusual bellows-boosted ailerons.[2]
[edit] Testing
The XP-79B (after delays because of bursting tires and brake problems on taxiing trials on the Muroc dry lake) was lost on its first flight 12 September 1945. While performing a slow roll 15 minutes into the flight, control was lost for unknown reasons. The nose dropped and the roll continued with the aircraft impacting in a vertical spin. Test pilot Harry Crosby attempted to bail out but was struck by the aircraft and fell to his death. Shortly thereafter, the project was cancelled.
[edit] Specifications (XP-79B)
Data from[citation needed]
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 14 ft 0 in (4.27 m)
Wingspan: 28 ft 0 in (8.54 m)
Height: 7 ft 0 in (2.13 m)
Wing area: 278 ft² (25.8 m²)
Empty weight: 5,840 lb (2,650 kg)
Loaded weight: 8,669 lb (3,932 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Westinghouse 19B turbojet, 1,150 lbf (5.1kN) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 547 mph (880 km/h)
Range: 993 mi (1,598 km)
Service ceiling: 40,000 ft (12,200 m)
Rate of climb: 4,000 ft/min (1,220 m/min)
Wing loading: 31 lb/ft² (153 kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 0.27
Armament
Guns: 4 × .50-cal (12.7 mm) machine guns (never fitted)
In 1942, John K. Northrop conceived the XP-79 as a high-speed rocket-powered flying-wing fighter aircraft.
In January 1943, a contract for three prototypes designation XP-79 was issued by the United States Army Air Forces.
To test the radical design, glider prototypes were built. One designated MX-324 was towed into the air on 5 July 1944 by a P-38 making it the first US-built rocket-powered aircraft to fly.[1]
Originally, it was planned to use a 2,000 lbf (9 kN) thrust XCALR-2000A-1 "rotojet" rocket motor supplied by Aerojet that used monoethyl aniline and red fuming nitric acid; because of the corrosive and toxic nature of the liquids, the XP-79 was built using a welded magnesium alloy monocoque structure (to protect the pilot if the aircraft was damaged in combat) with a ⅛ in (3 mm) skin thickness at the trailing edge and a ¾ in (19 mm) thickness at the leading edge. However, the rocket motor configuration using canted rockets to drive the turbopumps was unsatisfactory and the aircraft was, subsequently fitted with two Westinghouse 19-B (J30) turbojets instead. This led to changing the designation to XP-79B. After the failure of the rocket motor, further development of the first two prototypes, ended.
The pilot controlled the XP-79 through a tiller bar and rudders mounted below; intakes mounted at the wingtips supplied air for the unusual bellows-boosted ailerons.[2]
[edit] Testing
The XP-79B (after delays because of bursting tires and brake problems on taxiing trials on the Muroc dry lake) was lost on its first flight 12 September 1945. While performing a slow roll 15 minutes into the flight, control was lost for unknown reasons. The nose dropped and the roll continued with the aircraft impacting in a vertical spin. Test pilot Harry Crosby attempted to bail out but was struck by the aircraft and fell to his death. Shortly thereafter, the project was cancelled.
[edit] Specifications (XP-79B)
Data from[citation needed]
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 14 ft 0 in (4.27 m)
Wingspan: 28 ft 0 in (8.54 m)
Height: 7 ft 0 in (2.13 m)
Wing area: 278 ft² (25.8 m²)
Empty weight: 5,840 lb (2,650 kg)
Loaded weight: 8,669 lb (3,932 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Westinghouse 19B turbojet, 1,150 lbf (5.1kN) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 547 mph (880 km/h)
Range: 993 mi (1,598 km)
Service ceiling: 40,000 ft (12,200 m)
Rate of climb: 4,000 ft/min (1,220 m/min)
Wing loading: 31 lb/ft² (153 kg/m²)
Thrust/weight: 0.27
Armament
Guns: 4 × .50-cal (12.7 mm) machine guns (never fitted)