Irena Sendlerowa - Courage and valor
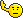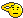
Irena Sendler, born in 1910, was raised by her Catholic parents to respect and love people regardless of their ethnicity or social status. Her father, a physician, died from typhus that he contracted during an epidemic in 1917. He was the only doctor in his town near Warsaw who would treat the poor, mostly Jewish victims of this tragic disease. As he was dying, he told 7-year-old Irena, "If you see someone drowning you must try to rescue them, even if you cannot swim." In 1939 the Nazis swept through Poland and imprisoned the Jews in ghettos where they were first starved to death and then systematically murdered in killing camps. Irena, by than a social worker in Warsaw, saw the Jewish people drowning nd resolved to do what she could to rescue as many as possible, especially the children. Working with a network of other social workers and brave Poles, mostly women, she smuggled 2,500 children out of the Warsaw ghetto and hid them safely until the end of the war. Sendler took great risks – obtaining forged papers for the children, disguising herself as an infection control nurse, diverting German occupation funds for the support of children in hiding. She entered the Warsaw ghetto, sometimes two and three times a day, and talked Jewish parents into giving up their children. Sendler drugged the babies with sedatives and smuggled them past Nazi guards in gunny sacks, boxes and coffins. She helped the older ones escape through the sewers, through secret openings in the wall, through the courthouse, through churches, any clever way she and her network could evade the Nazis. Once outside the ghetto walls, Sendler gave the children false names and documents and placed them in convents, orphanages and with Polish families. In 1942 the Polish underground organization ZEGOTA recruited her to lead their Children's Division, providing her with money and support. Her hope was that after the war she could reunite the children with surviving relatives, or at least return their Jewish identities. To that end she kept thin tissue paper lists of each child's Jewish name, their Polish name and address. She hid the precious lists in glass jars buried under an apple tree in the back yard of one of her co-conspirators. In 1943 Irena Sendler was arrested, tortured and sentenced to death by firing squad. She never divulged the location of the lists or her Polish underground contacts. At the last moment she was saved by ZEGOTA which bribed a guard to secure her freedom. She still bears the scars and disability of her torture. After the war, the Communist government suppressed any recognition of the courageous anti-fascist partisans, most of whom were also anti-Communists. Irena's story and those of other courageous Poles, were buried and forgotten. Her courage and resourcefulness were recognized by Israel in 1965 when she was awarded the Yad Vashem medal given to Righteous Gentiles who risked their own lives to save Jews during the Holocaust. In 1983 a tree was planted in her honor in Israel.
Irena Sendler, born in 1910, was raised by her Catholic parents to respect and love people regardless of their ethnicity or social status. Her father, a physician, died from typhus that he contracted during an epidemic in 1917. He was the only doctor in his town near Warsaw who would treat the poor, mostly Jewish victims of this tragic disease. As he was dying, he told 7-year-old Irena, "If you see someone drowning you must try to rescue them, even if you cannot swim." In 1939 the Nazis swept through Poland and imprisoned the Jews in ghettos where they were first starved to death and then systematically murdered in killing camps. Irena, by than a social worker in Warsaw, saw the Jewish people drowning nd resolved to do what she could to rescue as many as possible, especially the children. Working with a network of other social workers and brave Poles, mostly women, she smuggled 2,500 children out of the Warsaw ghetto and hid them safely until the end of the war. Sendler took great risks – obtaining forged papers for the children, disguising herself as an infection control nurse, diverting German occupation funds for the support of children in hiding. She entered the Warsaw ghetto, sometimes two and three times a day, and talked Jewish parents into giving up their children. Sendler drugged the babies with sedatives and smuggled them past Nazi guards in gunny sacks, boxes and coffins. She helped the older ones escape through the sewers, through secret openings in the wall, through the courthouse, through churches, any clever way she and her network could evade the Nazis. Once outside the ghetto walls, Sendler gave the children false names and documents and placed them in convents, orphanages and with Polish families. In 1942 the Polish underground organization ZEGOTA recruited her to lead their Children's Division, providing her with money and support. Her hope was that after the war she could reunite the children with surviving relatives, or at least return their Jewish identities. To that end she kept thin tissue paper lists of each child's Jewish name, their Polish name and address. She hid the precious lists in glass jars buried under an apple tree in the back yard of one of her co-conspirators. In 1943 Irena Sendler was arrested, tortured and sentenced to death by firing squad. She never divulged the location of the lists or her Polish underground contacts. At the last moment she was saved by ZEGOTA which bribed a guard to secure her freedom. She still bears the scars and disability of her torture. After the war, the Communist government suppressed any recognition of the courageous anti-fascist partisans, most of whom were also anti-Communists. Irena's story and those of other courageous Poles, were buried and forgotten. Her courage and resourcefulness were recognized by Israel in 1965 when she was awarded the Yad Vashem medal given to Righteous Gentiles who risked their own lives to save Jews during the Holocaust. In 1983 a tree was planted in her honor in Israel.