syscom3
Pacific Historian
Tonight marks the beginning of the first gunnery naval battle in which the USN were clear winners. Even then, luck played a part. But still, hats off to the bluejackets who earned this victory the hard way!
Background:
After the battle for Edson's Ridge, the Japanese set their next major attempt to recapture Henderson Field for October 20 and moved most of the 2nd and 38th Infantry Divisions, totalling 17,500 troops, from the Dutch West Indies to Rabaul in preparation for delivering them to Guadalcanal. Between September 14 and October 9, numerous Tokyo Express runs delivered troops from the Japanese 2nd Infantry Division as well as General Hyakutake to Guadalcanal. In addition to cruisers and destroyers, some of these runs included the Japanese seaplane tender Nisshin to deliver heavy equipment to the island including vehicles and heavy artillery other warships could not carry because of space limitations. The Japanese Navy promised to support the Army's planned offensive by delivering the necessary troops, equipment, and supplies to the island, and by stepping up air attacks on Henderson Field and sending warships to bombard the airfield.
In the meantime, Major General Millard F. Harmon, commander of United States Army forces in the South Pacific, convinced Vice Admiral Robert L. Ghormley, overall commander of Allied forces in the South Pacific, Marines on Guadalcanal needed to be reinforced immediately if the Allies were to successfully defend the island from the next expected Japanese offensive. Thus, on October 8, the 2,837 men of the 164th Infantry Regiment from the U.S. Army's Americal Division boarded ships at New Caledonia for the trip to Guadalcanal with a projected arrival date of October 13.
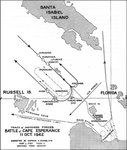
U.S. Rear Admiral Norman Scott.To protect the transports carrying the 164th to Guadalcanal, Ghormley ordered Task Force 64, consisting of four cruisers, USS San Francisco, USS Boise, USS Salt Lake City, and USS Helena, and five destroyers, USS Farenholt, USS Duncan, USS Buchanan, USS McCalla, and USS Laffey, under U.S. Rear Admiral Norman Scott, to intercept and combat any Japanese ships approaching Guadalcanal and threatening the convoy. Scott conducted one night battle practice with his ships on October 8, then took station south of Guadalcanal near Rennell Island on October 9, to await word of any Japanese naval movement towards the southern Solomons.
Continuing with preparations for the October offensive, Japanese Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa's Eighth Fleet staff, headquartered at Rabaul, scheduled a large and "singularly important" Tokyo Express supply run for the night of October 11. Nisshin would be joined by seaplane tender Chitose to deliver 728 soldiers, four large howitzers, two field guns, one antiaircraft gun, and a large assortment of ammunition and other equipment from the Japanese naval bases in the Shortland Islands and at Buin, Bougainville, to Guadalcanal. Six destroyers, five of them carrying troops, would accompany Nisshin and Chitose. The supply convoy, called the Reinforcement Group by the Japanese, was under the command of Rear Admiral Takatsugu Jojima. At the same time but in a separate operation the three heavy cruisers of Cruiser Division 6 (CruDiv6), Aoba, Kinugasa, and Furutaka, under the command of Rear Admiral Aritomo Gotō, were to bombard Henderson Field with special explosive shells with the object of destroying the CAF and the airfield's facilities. Two screening destroyers, Fubuki and Hatsuyuki, accompanied CruDiv6. Since U.S. Navy warships had yet to attempt to interdict any Tokyo Express missions to Guadalcanal, the Japanese were not expecting any opposition from U.S. naval surface forces that night
Prelude
Japanese Rear Admiral Aritomo Gotō.At 08:00 on Sunday, October 11, Jojima's reinforcement group departed the Shortland Islands anchorage to begin their 250 miles (402 km) run down the Slot to Guadalcanal. The six destroyers that accompanied Nisshin and Chitose included Asagumo, Natsugumo, Yamagumo, Shirayuki, Murakumo, and Akizuki. Gotō departed the Shortland Islands for Guadalcanal at 14:00 the same day.
To protect the reinforcement group's approach to Guadalcanal from the CAF, the Japanese 11th Air Fleet, based at Rabaul, Kavieng, and Buin, planned two air strikes on Henderson Field for October 11. A "fighter sweep" of 17 A6M Zeros swept over Henderson Field just after mid-day but failed to engage any U.S. aircraft. Forty-five minutes later the second wave, 45 "Betty" bombers and 30 Zeros, arrived over Henderson Field. In an ensuing air battle with the CAF, one Betty and two U.S. fighters were downed. Although the Japanese attacks failed to inflict significant damage, they did prevent CAF bombers from finding and attacking the reinforcement group. As the reinforcement group transited the Slot, relays of 11th Air Fleet Zeros from Buin provided escort. Emphasizing the importance of this convoy for Japanese plans, the last flight of the day was ordered to remain on station over the convoy until darkness, then ditch their aircraft and await pickup by the reinforcement group's destroyers. All six Zeros ditched; only one pilot was recovered.
Allied reconnaissance aircraft sighted Jojima's supply convoy 210 miles from Guadalcanal between Kolombangara and Choiseul in the Slot at 14:45 on the same day and reported it as two "cruisers" and six destroyers. Gotō's force, following the convoy, was not sighted. In response to the sighting of Jojima's force, at 16:07 Scott turned toward Guadalcanal for an interception.
Up to this point, the Allies had lost every surface night battle with the Japanese navy, losing eight cruisers and three destroyers without sinking a single Japanese warship. Aware of the Japanese advantage in night fighting, Scott crafted a simple battle plan for the expected engagement. His ships would steam in column with his destroyers at the front and rear of his cruiser column. The destroyers were to illuminate any targets with searchlights and discharge torpedoes while the cruisers were to open fire at any available targets without awaiting orders. The cruiser's float aircraft, launched in advance, were to find and illuminate the Japanese warships with flares. Although Helena and Boise carried the new, greatly improved SG radar, Turner chose San Francisco as his flagship.
At 22:00, as Scott's ships neared Cape Hunter at the northwest end of Guadalcanal, three of Scott's cruisers launched floatplanes. One crashed on takeoff, but the other two patrolled over Savo Island, Guadalcanal, and Ironbottom Sound. As the floatplanes were launched, Jojima's force was just passing around the mountainous northwestern shoulder of Guadalcanal, and neither force sighted each other. At 22:20, Jojima radioed Gotō and told him that no U.S. ships were in the vicinity. Although Jojima's force later heard Scott's floatplanes overhead while unloading along the north shore of Guadalcanal, they failed to report this to Gotō.
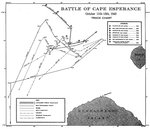
At 22:33, just after passing Cape Esperance, Scott's ships assumed battle formation. The column was led by Farenholt, Duncan, and Laffey, and followed by San Francisco, Boise, Salt Lake City, and Helena. Buchanan and McCalla brought up the rear. The distance between each ship ranged from 500 yards to 700 yards. Visibility was poor because the moon had already set, leaving no ambient light and no visible sea horizon.
Gotō's force passed through several rain squalls as they approached Guadalcanal at 30 knots. Gotō's flagship Aoba led the Japanese cruisers in column, followed by Furutaka and Kinugasa. Fubuki was starboard of Aoba and Hatsuyuki to port. At 23:30, Gotō's ships emerged from the last rain squall and began appearing on the radar scopes of Helena and Salt Lake City. The Japanese, however, remained unaware of Scott's presence.