Flight Lieutenant Eric Atkins 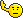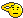
Flight Lieutenant Eric Atkins, who has died aged 90, flew 60 low-level bombing raids with a Polish Mosquito squadron and was twice decorated with the DFC; he also won the Polish Cross of Valour on two occasions.
Atkins was transferred to No 305 Squadron in April 1944 after it had suffered heavy losses. Most of the crews were Polish, and he usually flew with a Polish navigator, Flight Lieutenant Jurek Meyer.
The squadron flew night intruder missions over northern France and Belgium as a prelude to the D-Day landings, attacking enemy road traffic, railways and canals. On D-Day itself, Atkins attacked trains in the Cherbourg area; thereafter he was in action every night, targeting the German reinforcements making for the Normandy bridgehead .
As the Allied armies prepared to break out of Normandy, Atkins attacked a German Panzer Division, and on August 25 he took part in a major assault on enemy troops massing near the river Seine. That night he completed three sorties, and five days later his was one of six crews which severely damaged a fuel storage depot near Nancy. Shortly afterwards he was awarded the first of his DFCs.
As the Allied armies prepared to break out of Normandy, Atkins attacked a German Panzer Division, and on August 25 he took part in a major assault on enemy troops massing near the river Seine. That night he completed three sorties, and five days later his was one of six crews which severely damaged a fuel storage depot near Nancy. Shortly afterwards he was awarded the first of his DFCs.
The Allies were now moving eastwards, and Atkins and his Polish colleagues bombed troop movements in Belgium and western Germany, then ranged deeper into Germany to bomb and strafe railways, road convoys and troop reinforcements. He was awarded a Polish Cross of Valour. In November the squadron moved to an airfield in France, from where it continued to attack trains and canal traffic. After suffering damage from anti-aircraft fire, Atkins was forced to land his Mosquito at night without the undercarriage and with fused bombs still in the bomb bay. It was half an hour before the crash rescue crews would venture close to the wrecked aircraft.
After a highly successful operation against Panzer units at Wassenburg in December, Atkins was rested. He had completed 78 operations, most of them alongside the Poles. He was awarded a Bar to his DFC, and a Bar to his Cross of Valour. The Poles also awarded him the Squadron Badge of Honour and the Polish Air Force Medal. (He received his two DFCs from a clerk in the Air Ministry.) Atkins greatly admired his Polish comrades, later writing of them; "[They] were magnificent people and fierce warriors, and their ground crews were devoted and dedicated."
The son of a mining engineer, Eric Granville Albert Atkins was born at Mansfield on March 19 1921. After the family moved to Essex, he went to South-East Essex College, leaving when he was 14 to work for Unilever.
A keen Boy Scout, he was curious about the Hitler Youth and arranged a holiday in Germany. He was escorted to a number of camps but became increasingly uncomfortable with the atmosphere and anti-British feeling. Then he received a telegram from home reading "Brother very ill, return home immediately, Father". He had no brother, but excused himself, hitchhiked to Calais and landed at Dover to find newspaper billboards declaring "War with Germany".
Atkins joined the Civil Defence before being accepted for service as a pilot with the RAF. In September 1941 he joined No 139 Squadron, flying Blenheim bombers on anti-shipping patrols off the Dutch coast and daylight bombing operations over northern France. In November he and his crew flew a Blenheim to Gibraltar. Their next task was to rendezvous in the Mediterranean with the carrier Ark Royal, wait for 26 Hurricanes to be launched and then escort them on the long flight to Malta.
After returning to England, Atkins flew night operations but was injured when his Blenheim crash-landed after being badly damaged by anti-aircraft fire. He became an instructor on medium bombers and was commissioned.
Early in 1944 he returned to operations to fly the Mosquito with No 464 (RAAF) Squadron in the low-level attack role. During the spring he attacked the V-1 launching sites in the Pas de Calais region before transferring to No 305 Squadron in April.
After completing his service with the Poles, Atkins became a test pilot with a repair and salvage unit before becoming personal pilot to General GI Thomas, GOC 1st British Corps in Germany. He left the RAF in 1946.
Atkins returned to Unilever, becoming regional sales manager in south London before moving as a manager to the European sales division.
In his sixties he took up climbing, and he was founder-chairman of the Mosquito Aircrew Association.
Eric Atkins married, in 1950, Sheila Finlay-Day, who survives him with their son and daughter.
Flight Lieutenant Eric Atkins, born March 19 1921, died November 22 2011.
source: The Telegraph

Flight Lieutenant Eric Atkins, who has died aged 90, flew 60 low-level bombing raids with a Polish Mosquito squadron and was twice decorated with the DFC; he also won the Polish Cross of Valour on two occasions.
Atkins was transferred to No 305 Squadron in April 1944 after it had suffered heavy losses. Most of the crews were Polish, and he usually flew with a Polish navigator, Flight Lieutenant Jurek Meyer.
The squadron flew night intruder missions over northern France and Belgium as a prelude to the D-Day landings, attacking enemy road traffic, railways and canals. On D-Day itself, Atkins attacked trains in the Cherbourg area; thereafter he was in action every night, targeting the German reinforcements making for the Normandy bridgehead .
As the Allied armies prepared to break out of Normandy, Atkins attacked a German Panzer Division, and on August 25 he took part in a major assault on enemy troops massing near the river Seine. That night he completed three sorties, and five days later his was one of six crews which severely damaged a fuel storage depot near Nancy. Shortly afterwards he was awarded the first of his DFCs.
As the Allied armies prepared to break out of Normandy, Atkins attacked a German Panzer Division, and on August 25 he took part in a major assault on enemy troops massing near the river Seine. That night he completed three sorties, and five days later his was one of six crews which severely damaged a fuel storage depot near Nancy. Shortly afterwards he was awarded the first of his DFCs.
The Allies were now moving eastwards, and Atkins and his Polish colleagues bombed troop movements in Belgium and western Germany, then ranged deeper into Germany to bomb and strafe railways, road convoys and troop reinforcements. He was awarded a Polish Cross of Valour. In November the squadron moved to an airfield in France, from where it continued to attack trains and canal traffic. After suffering damage from anti-aircraft fire, Atkins was forced to land his Mosquito at night without the undercarriage and with fused bombs still in the bomb bay. It was half an hour before the crash rescue crews would venture close to the wrecked aircraft.
After a highly successful operation against Panzer units at Wassenburg in December, Atkins was rested. He had completed 78 operations, most of them alongside the Poles. He was awarded a Bar to his DFC, and a Bar to his Cross of Valour. The Poles also awarded him the Squadron Badge of Honour and the Polish Air Force Medal. (He received his two DFCs from a clerk in the Air Ministry.) Atkins greatly admired his Polish comrades, later writing of them; "[They] were magnificent people and fierce warriors, and their ground crews were devoted and dedicated."
The son of a mining engineer, Eric Granville Albert Atkins was born at Mansfield on March 19 1921. After the family moved to Essex, he went to South-East Essex College, leaving when he was 14 to work for Unilever.
A keen Boy Scout, he was curious about the Hitler Youth and arranged a holiday in Germany. He was escorted to a number of camps but became increasingly uncomfortable with the atmosphere and anti-British feeling. Then he received a telegram from home reading "Brother very ill, return home immediately, Father". He had no brother, but excused himself, hitchhiked to Calais and landed at Dover to find newspaper billboards declaring "War with Germany".
Atkins joined the Civil Defence before being accepted for service as a pilot with the RAF. In September 1941 he joined No 139 Squadron, flying Blenheim bombers on anti-shipping patrols off the Dutch coast and daylight bombing operations over northern France. In November he and his crew flew a Blenheim to Gibraltar. Their next task was to rendezvous in the Mediterranean with the carrier Ark Royal, wait for 26 Hurricanes to be launched and then escort them on the long flight to Malta.
After returning to England, Atkins flew night operations but was injured when his Blenheim crash-landed after being badly damaged by anti-aircraft fire. He became an instructor on medium bombers and was commissioned.
Early in 1944 he returned to operations to fly the Mosquito with No 464 (RAAF) Squadron in the low-level attack role. During the spring he attacked the V-1 launching sites in the Pas de Calais region before transferring to No 305 Squadron in April.
After completing his service with the Poles, Atkins became a test pilot with a repair and salvage unit before becoming personal pilot to General GI Thomas, GOC 1st British Corps in Germany. He left the RAF in 1946.
Atkins returned to Unilever, becoming regional sales manager in south London before moving as a manager to the European sales division.
In his sixties he took up climbing, and he was founder-chairman of the Mosquito Aircrew Association.
Eric Atkins married, in 1950, Sheila Finlay-Day, who survives him with their son and daughter.
Flight Lieutenant Eric Atkins, born March 19 1921, died November 22 2011.
source: The Telegraph
